- Using Recursion
- Using Bitset
Problem Statement: Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example: Input:
nums = [1,2,3]
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
Solution
1. Using Recursion
Firstly, I'll be discussing recursive approach to subset finding problem. Recursive problem is easy to visualise. Consider the given testcase[1, 2, 3].
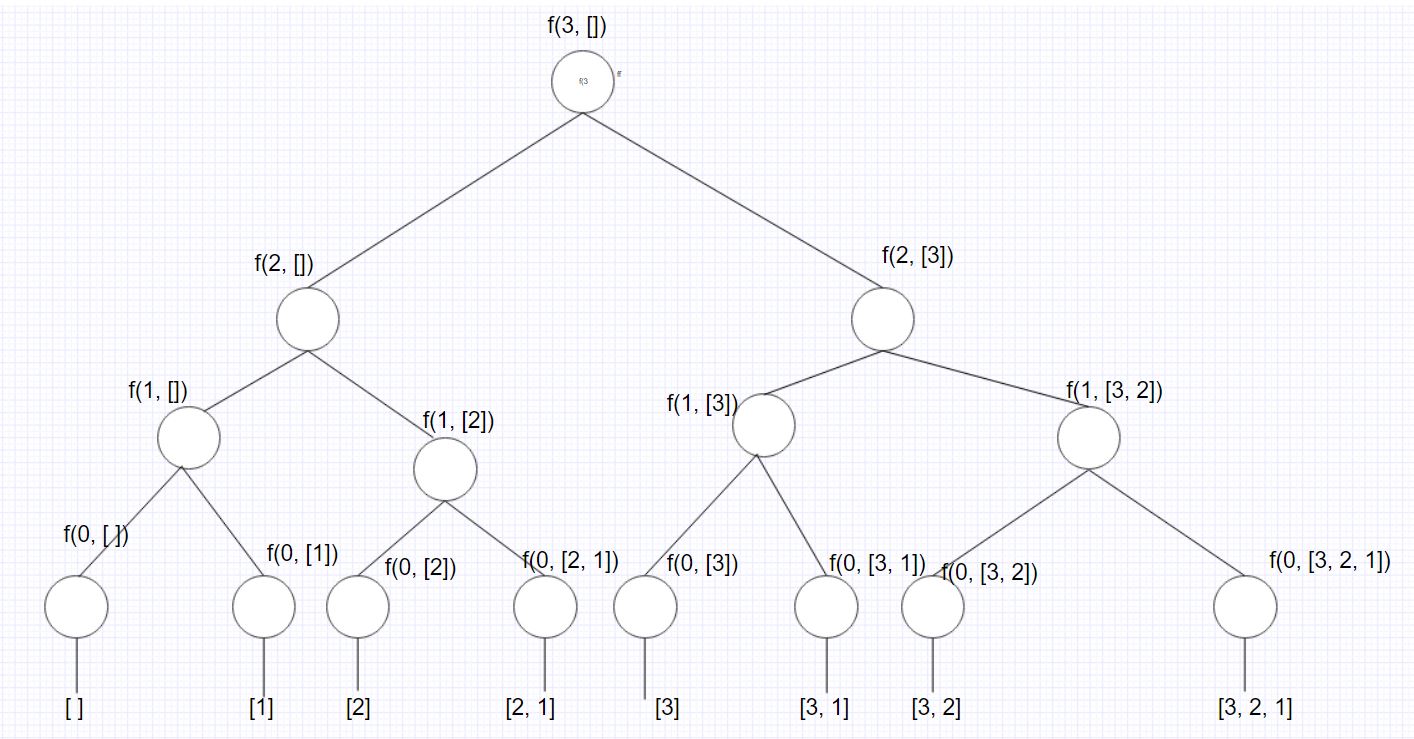 Let
Let solve(nums, n, subset) be the function that find subsets for array nums and number of elements n, initially called with an empty subset.
So our initial call is :vector<int>subset;
solve(nums, nums.size(), subset);
Recursive Cases: For every state i.e
(n), i,e position n - 1 of solve(nums, n, subset)
- Don’t include the current element in the subset i.e simply call
solve(nums, n - 1, subset);
subset.push_back(arr[n - 1]);
solve(nums, n - 1, subset);
Let’s think of base cases. The base cases are:
- If
n == 0i.e no item left push the currentsubsetto oursubsets_which is a vector of vector.
if (n == 0){ subsets_.push_back(subset); return; }
class Solution { public: // Vector of vector of int to store all the subsets vector<vector<int>> subsets_; // Solve method that generates subset recursively void solve(vector<int> &nums, int n, vector<int> subset){ // If size of array becomes 0, no elemnts are left // We push current subset to our subsets_ and return if (n == 0){ subsets_.push_back(subset); return; } // Else we have 2 options: // Don't include the current element to subset solve(nums, n - 1, subset); // Incldue the current element in subset subset.push_back(nums[n - 1]); solve(nums, n - 1, subset); } // Solution method subsets vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) { // Make an empty vector subset vector<int> subset; // Call solve function initially with an empty subset solve(nums, nums.size(), subset); // Return subsets after calculation return subsets_; } };
2. Using Bitset
I have explained the bitset method on quora.
0 comments:
Post a Comment